Physics A block of mass m 200 kg is attached to a spring of force constant k 515 102 Nm that lies on a horizontal frictionless surface as shown in the figure below. 0 N and m 2.
Solved Q1 A A 6 0 Kg Block Initially At Rest Is Pulled To Chegg Com
Find the speed of the block after it has moved 30 m.

. What is true of the friction acting on the block after a time of 1 second. 5 kg is the mass of the block. To what maximum height does the block then rise above its initial position.
A What is the maximum compression if the spring. How much kinetic energy does the block gain. Use the work-kinetic energy theorem to find the blocks.
This pendulum is released from rest with the string horizontal. A Find the speed of the block after it has moved 30 m if the surfaces in contact have a coefficient of kinetic friction of 015. A Static friction acts upward on the block.
This implies f s m a x μ s F N 6. 0 N rightward force. 8 m s 2 1 0 N 1 4.
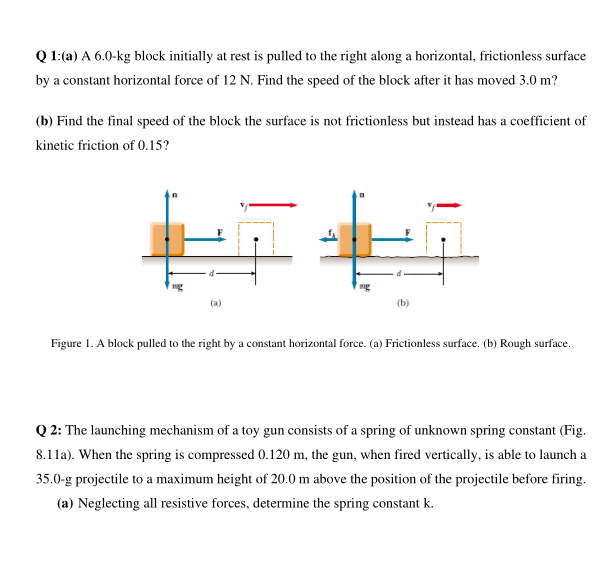
The pulley has a mass of 30-kg radius of 10 cm and rotates about the symmetry axis through its center. 0 N leads to F N 2. Example 84 A Block Pulled on a Rough Surface A 60-kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a horizontal surface by a constant horizontal force of 12 N.
The coefficient of kinetic friction is 030 while the coefficient of static friction is 050. The bullet emerges from the block moving directly upward at 400 ms. 5 k g 9.
Find the blocks speed after it has moved 3 m. Where F 6. A 60 kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a horizontal surface having a coefficient of kinetic friction of 015 by a constant horizontal force of 12N.
Speed after it has moved 30 m. Find the speed of the block after it has moved 30 m. B Suppose the force F is applied at an angle θ.
Use the work-kinetic energy theorem to find the block s. A frictionless horizontal surface by a constant horizontal force. Thus the block which was.
A 60kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a horizontal frictionless surface by a constant horizontal force of 12 N. Find the speed of the block after it has moved 30 m. The horizontal track including the portion under the spring has a kinetic coefficient of friction 01.
A 60-kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a horizontal frictionless surface by a constant horizontal force of 12 N. 5 A 6 kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a frictionless horizontal surface by a constant horizontal force of 12 N. 5 x 2 i N where x is in meters and the initial position of the block is x 0a What is the kinetic energy of the block as it passes through x 20 m.
A 60-kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a horizontal surface by a constant horizontal force of 12 N. A Find the speed of the block using work-kinetic energy theorem after it has moved 30 m. Solution for A 6 kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a rough surface cl by a constant horizontal force of F 12 N at an angle 0 30 as Answered.
6 N which is larger than the 6. Suppose a 6 kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a horizontal surface by a constant horizontal force of 12 N. Find the speed of the block after it has moved 3m.
Take k30Nm b where does the block ultimately comes to rest. Find the speed of the block after it has moved 30 m if the surface. This is Example 77 modified so that the surface is no longer frictionless B Suppose the force F is applied at an angle θ as shown in.
A 060-kg block initially at rest on a frictionless horizontal surface is acted upon by a force of 40 N for a distance of 65 m. HW Set VI page 2 of 9 PHYSICS 1401 1 homework solutions. A 200kg block initially at rest is released from point A as shown.
A 60-kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a frictionless horizontal surface by a constant horizontal force of 12 N. A 6-kg block m initially at rest on a rough shelf is connected to a 4-kg block m2 that hangs by an inextensible string of negligible mass passing over a uniform ring-shaped pulley. V 316 ms.
A 60 kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a horizontal frictionless surface by a constant horizontal force of 12 N. 8 A 60-kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along. Find the speed of the block after it has moved 30 m.
Fundamentals of Physics EXP-2928 A 60-kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a horizontal frictionless surface by a constant horizontal force of 12 N. A 6 kg block initially at rest is bartleby. The force is given by F x 2.
Through the center of mass of a 50 kg block initially at rest Fig. 16-kg ball is attached to the end of a 040-m string to form a pendulum. A 60kg block initially at rest is pulled to the right along a horizontal frictionless surface by a constant horizontal force of 12 N.
A Find the speed of the block after it has moved 30 m if the surfaces in contact have a coefficient of kinetic friction of 015. At the lowest point of its swing when it is moving horizontally the ball collides with a 080-kg block initially at rest on a. A 15 kg block is initially at rest on a horizontal frictionless surface when a horizontal force along the x-axis is applied to the block.
A In this case P 8. A 60 kg block initially at rest is pushed against a wall by a 100 N force as shown. The curved portion of the track is frictionless.
B Kinetic friction acts upward on the block.

Program Of Physics Lecturer Dr Do Xuan Hoi Room Ppt Download

Phy 151 Lecture Nonisolated System Energy Ppt Download

A 6 0 Kg Block Initially At Rest Is Pulled To The Right Along A Horizontal Frictionless
0 Comments